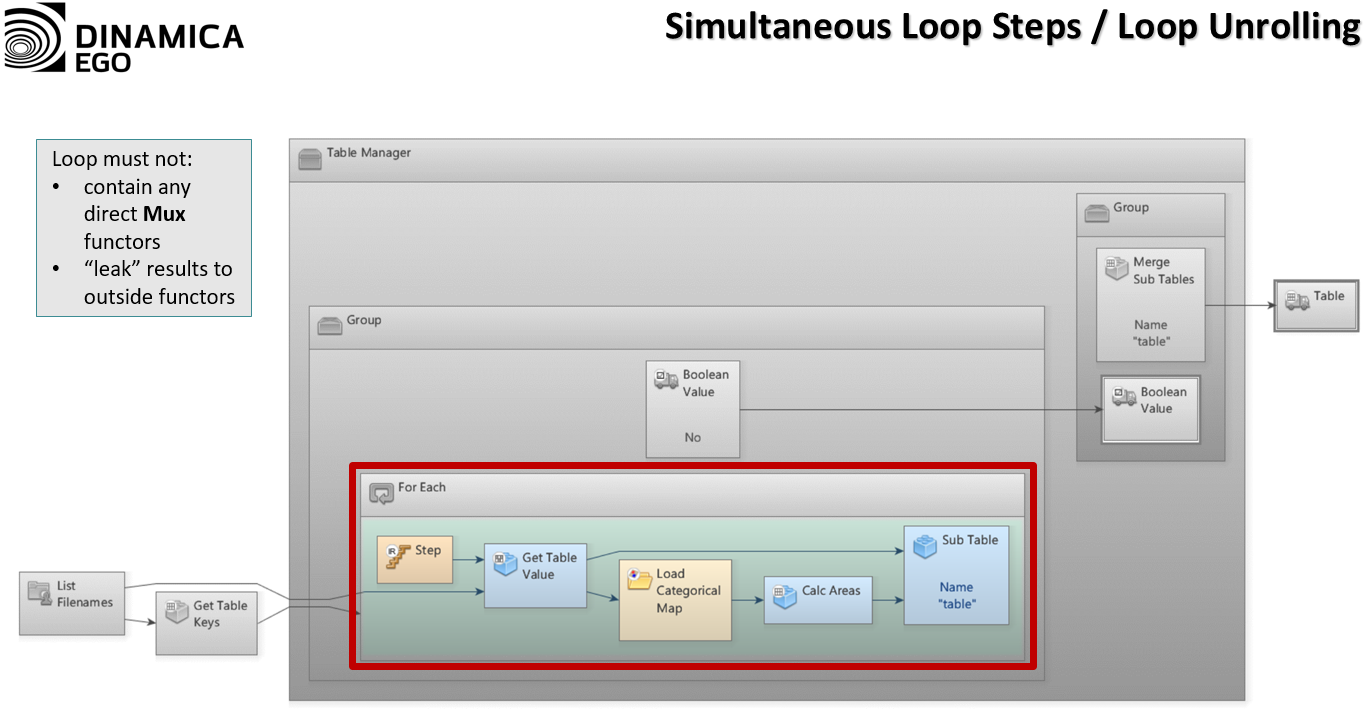
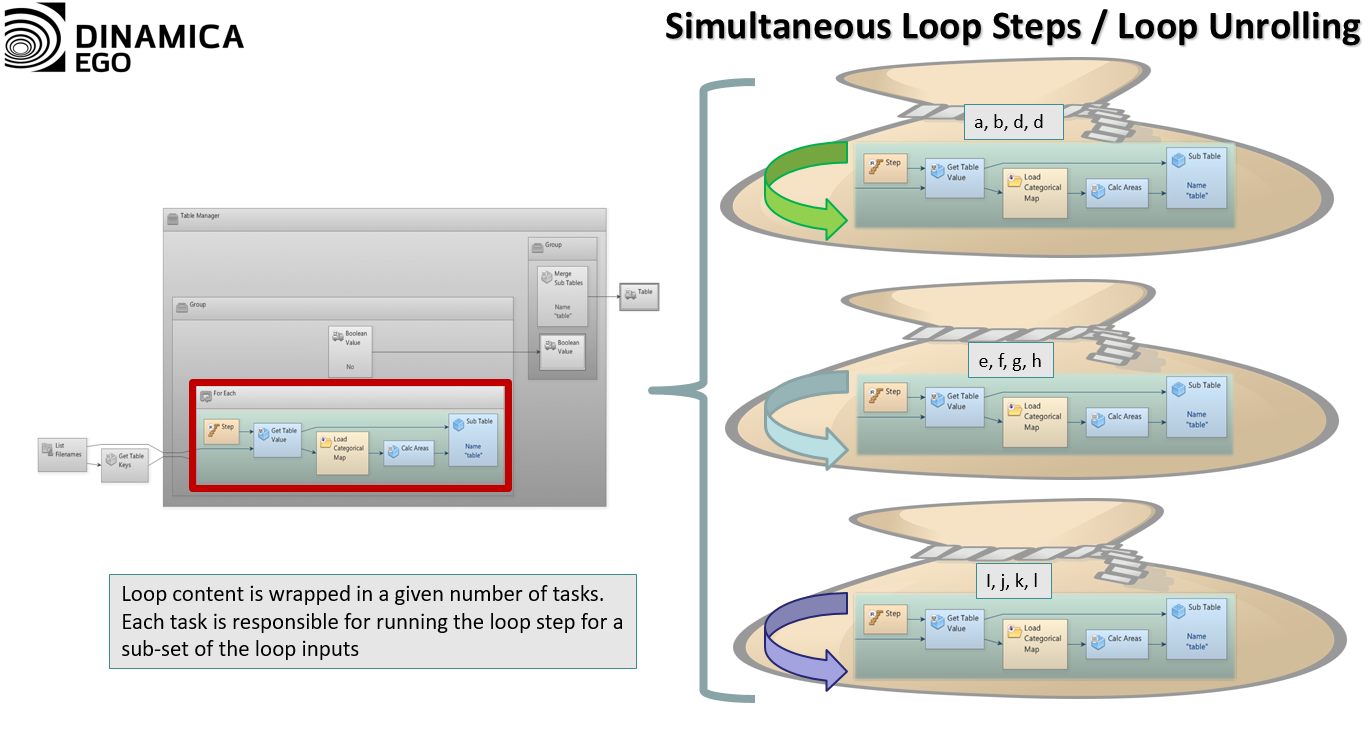
This is an old revision of the document!
Parallelism on Dinamica EGO
What is Parallelism?
The term Parallelism (in Computer Science) refers to a technique that allow two or more computing tasks to execute at the same time. This requires hardware with multiple processing units. A key problem of parallelism is to reduce data dependencies in order to be able to perform computations on independent computation units with minimal communication between them. To this end, it can even be an advantage to do the same computation twice on different units.
How can Parallelism be achieved in modern systems?
On modern systems, parallelism can be achieve in two different ways:
• By executing tasks in the same time slice (and pausing the inactive tasks to give an impression of concurrency);
• By having multiple processing units that physically execute tasks simultaneously.
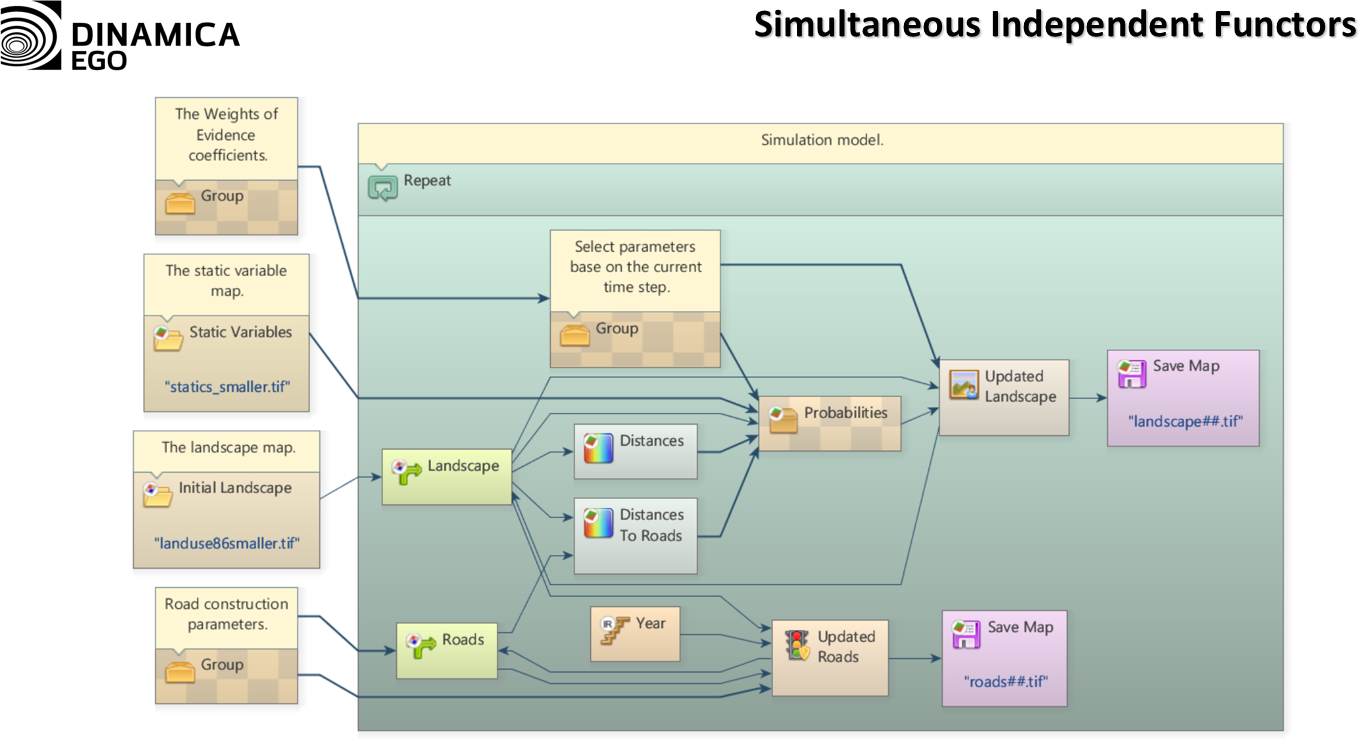
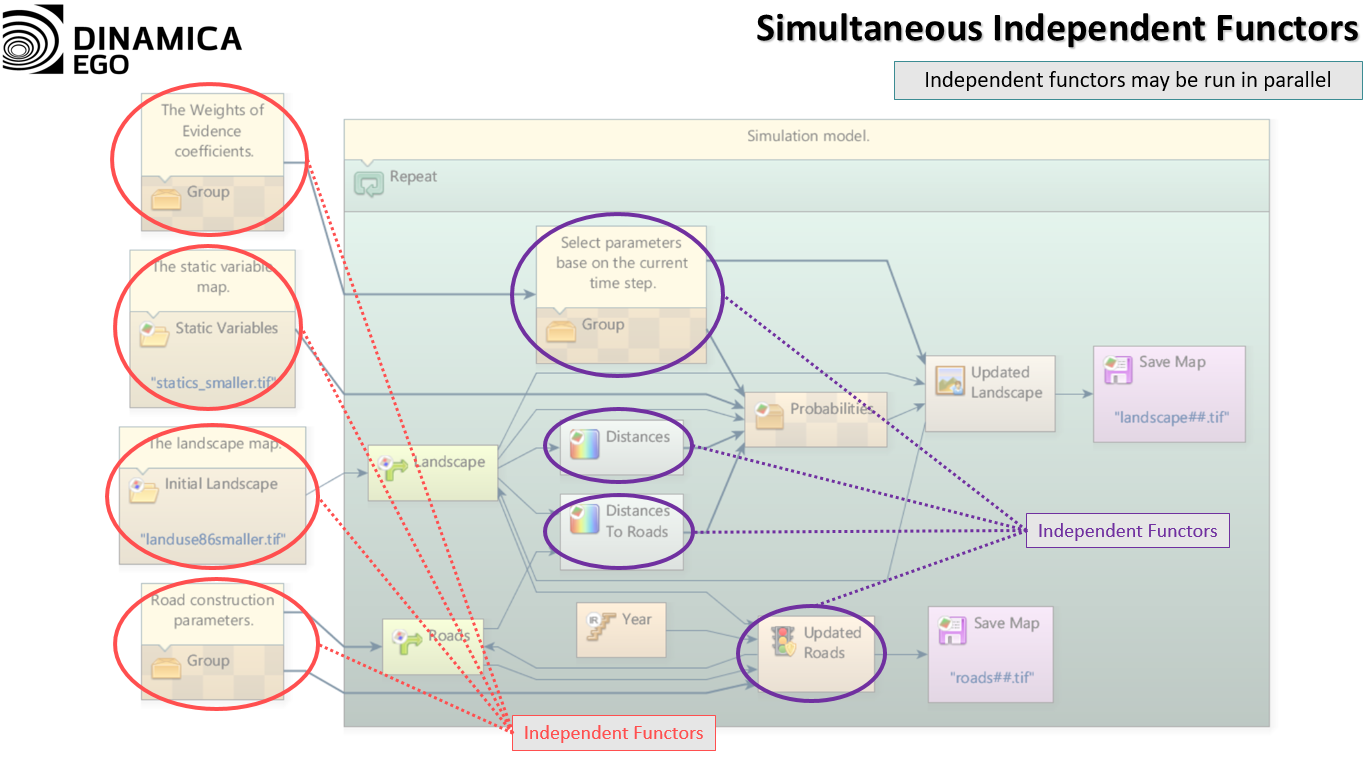
Since modern processor architectures are composed of many cores, the later method strongly surpasses the former in terms of speed and ease of programming. In such systems, programmers must adapt their software to take advantage of Parallelism, taking into account concurrent access to data. To do that, data is usually broken into equal independent slices that are processed in different computing units but a fundamental problem arises when this data is not easily separable or is dependent of many computing iterations. In order to deal with this situation, software developers and architects developed many algorithms and techniques to minimize communication between computing units and data dependency. To this end, it can even be an advantage to do the same computation twice on different units to prevent synchronization.
Why is Parallelism important?
Efficiently using these parallel capabilities is necessary to meet user demands for modelling complex dynamics with large datasets. However, users may be reticent to develop or adapt their current models to take advantage of these parallel environments because such development is often complicated, time-consuming, and error prone.
Graphic computations on a GPU are parallelism!
Besides the general purpose processors, another class of devices like the GPUs are able to offer Parallelism. Such devices can provide a greater level of concurrent operations due to the higher number of processors when compared to traditional CPUs. Since GPU processors are dedicated to certain type of tasks, those devices also need their own set of programming rules and data access.
How we change Dinamica EGO infrastructure and make everything as much parallel as possible?
Specifically, we re-designed the software to leverage available parallel hardware capabilities on any computer, while maintaining flexibility for the user to develop custom models without worrying about such parallelization.
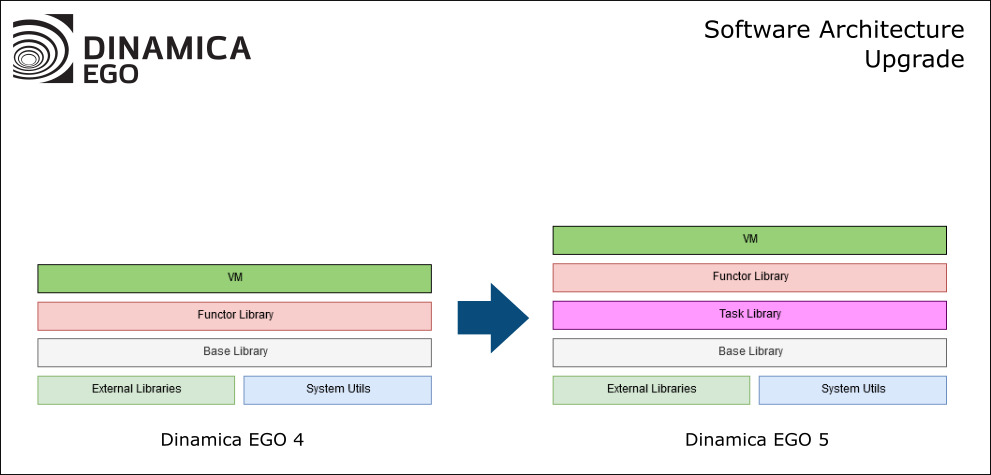
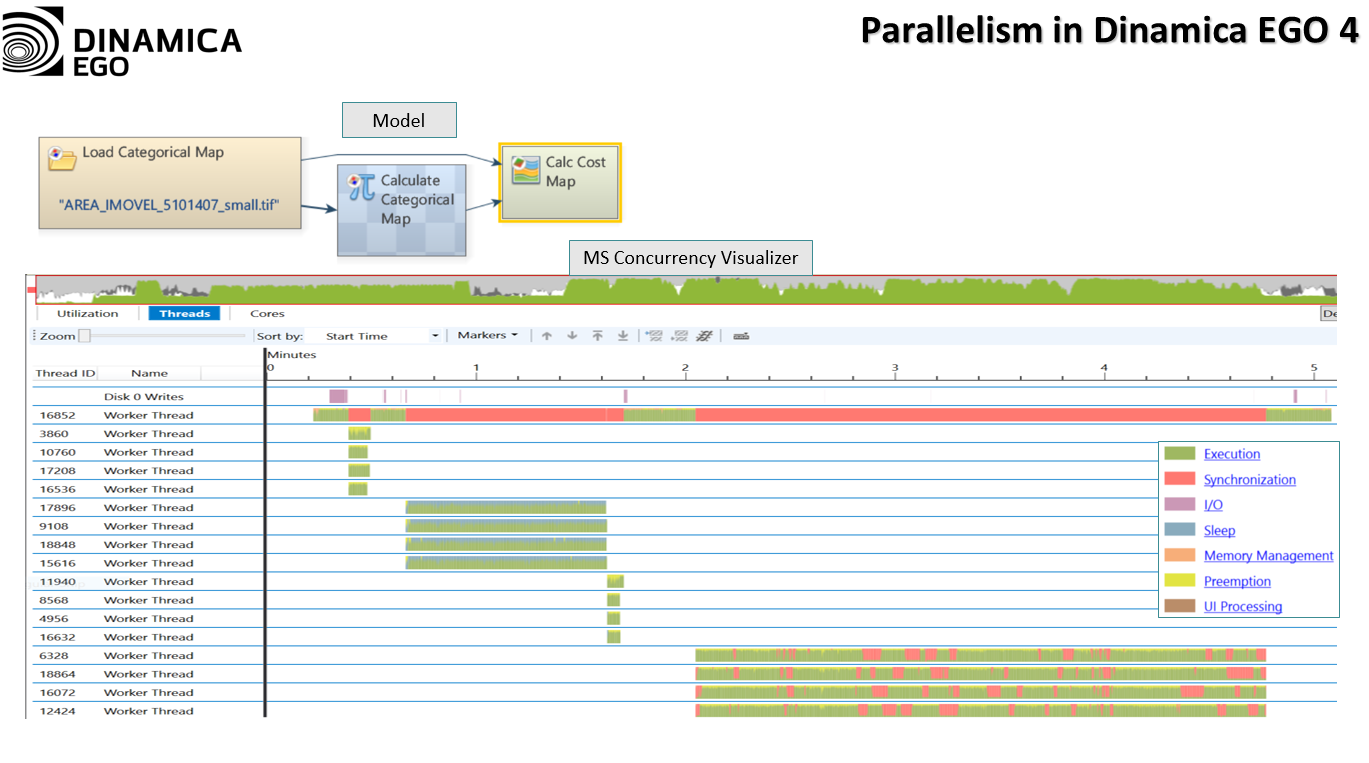
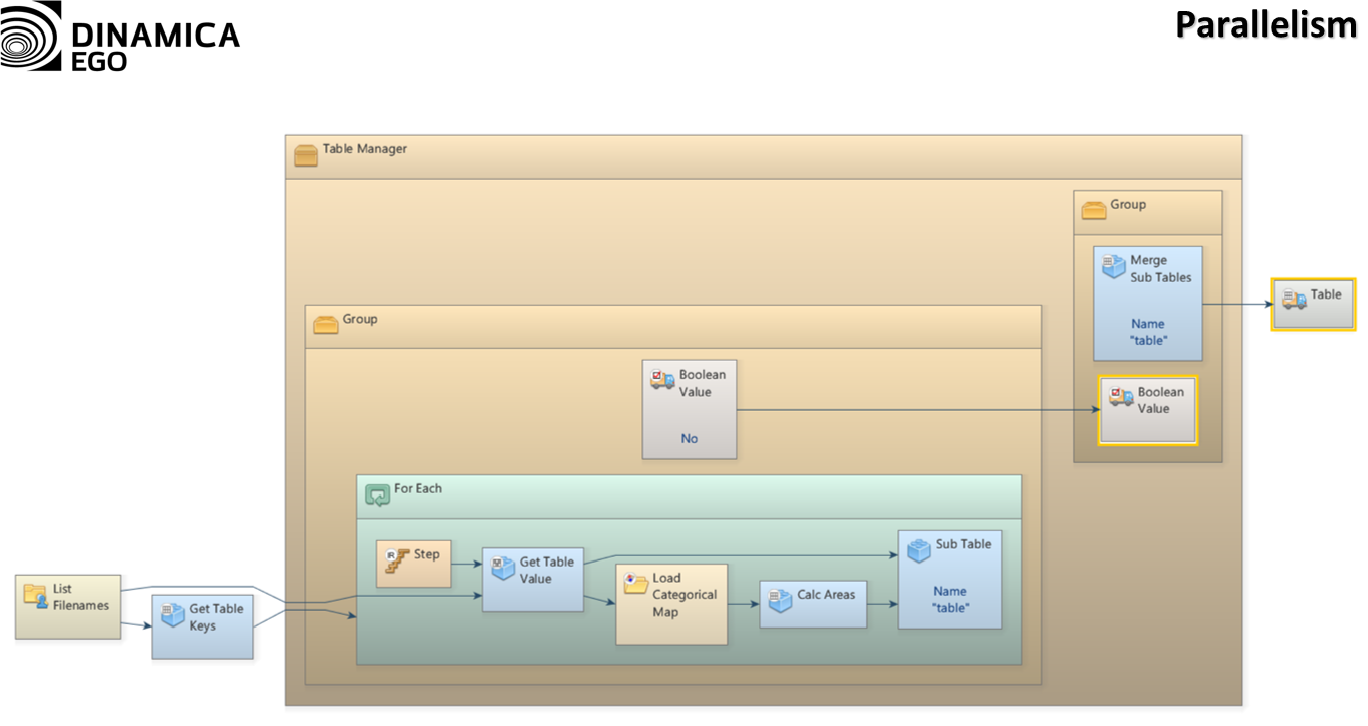
We restructured the core of the software so that models are now broken into tasks according to computer capabilities and model semantics (i.e., the rules the computer must follow as prescribed by the model). Tasks are then executed by a fixed number of “workers” using a
work-stealing approach. These workers can manipulate data in parallel (e.g., parts of an image can be read and written simultaneously) and compute certain tasks using graphics processing units.
Tasks + Work Stealing in Dinamica EGO 5